.webp)
The European Union (EU) is home to a diverse set of economies, each with its own currency history, financial regulations, and banking systems. While the EU has made significant strides in creating a single market and harmonizing financial services through initiatives like SEPA (Single Euro Payments Area), cross-border payments still pose significant challenges within and outside the eurozone.
The rise of Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies has sparked a new conversation around how digital currencies might revolutionize cross-border payments. Bitcoin, with its decentralized and borderless nature, offers the potential for faster, cheaper, and more transparent transactions across Europe and beyond. However, the road to full adoption is not without its hurdles.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the current cross-border payment challenges in the EU and analyze whether Bitcoin can serve as a viable solution.
Current Cross-Border Payment Challenges in the EU
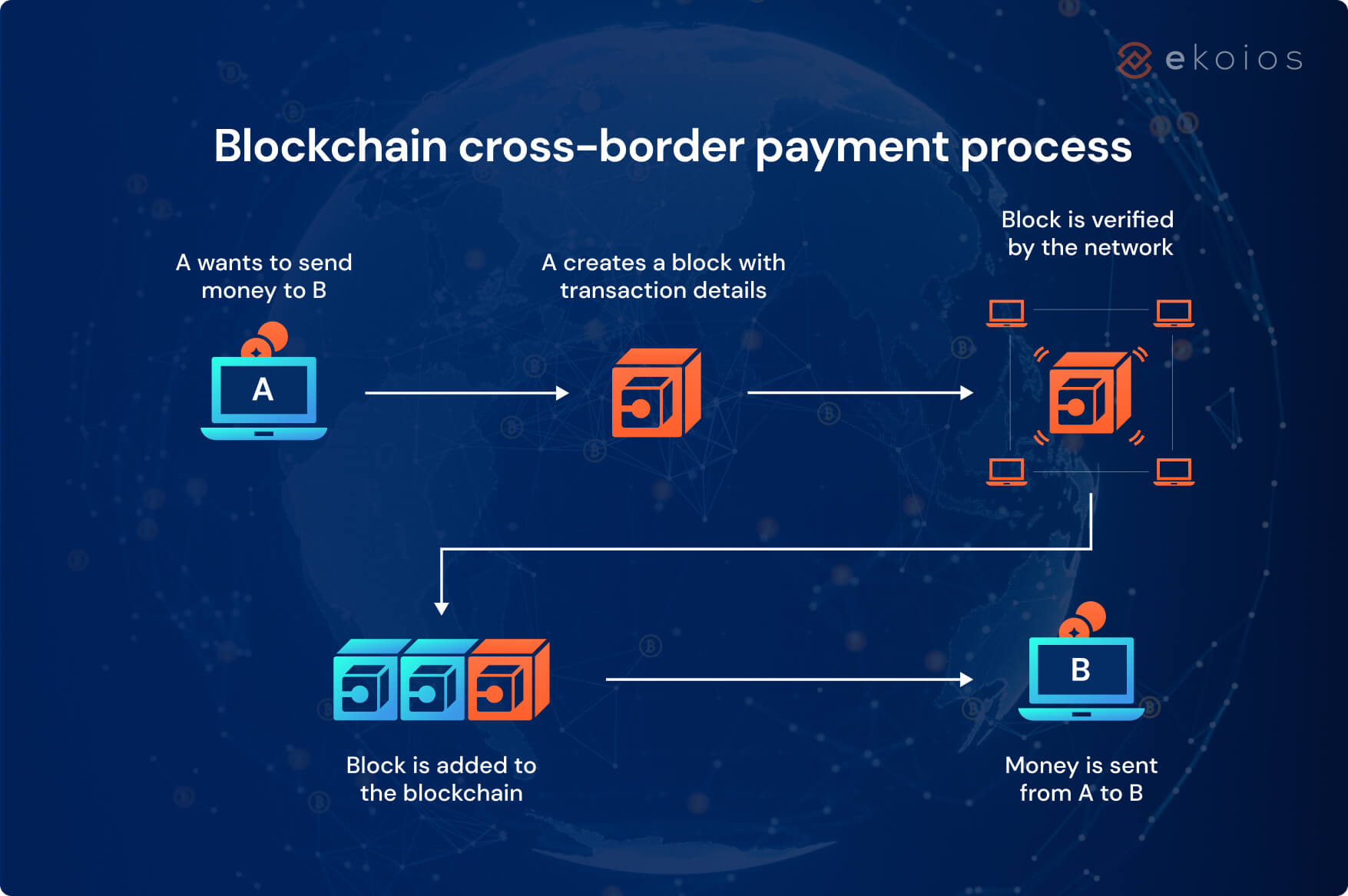
Despite the progress made in simplifying payments across Europe, several challenges still remain when it comes to cross-border payments:
- High Fees
Traditional cross-border payments, especially those involving currencies outside the eurozone, often come with high fees. Banks and money transfer services charge for conversion, handling, and intermediary processing, making international transfers expensive for individuals and businesses alike. - Slow Processing Times
Although the SEPA system has streamlined euro transactions across member states, payments involving non-eurozone currencies or those that cross European borders can still take days to process. This is especially true when transactions pass through multiple banks or payment processors. - Currency Conversion Issues
Payments involving multiple currencies often require conversions, which can be complicated and costly. Exchange rates can fluctuate rapidly, and users are frequently unaware of the exact fees they’ll incur, making the process less transparent. - Limited Access to Banking Services
Not all individuals and businesses in the EU have easy access to banking services, particularly in countries with less developed financial infrastructure. This can create bottlenecks for cross-border trade and limit economic participation.
How Bitcoin Could Address These Challenges

Bitcoin’s decentralized, peer-to-peer network offers a number of potential solutions to the issues outlined above. Here are the key ways Bitcoin could solve cross-border payment challenges in the EU:
- Lower Transaction Fees
One of Bitcoin’s major advantages is its ability to reduce transaction fees, especially for cross-border payments. Unlike traditional banking systems that involve intermediaries at multiple points, Bitcoin transactions are direct between users on the network. This eliminates the need for banks, clearinghouses, and other middlemen, significantly lowering fees.
While Bitcoin transactions still come with fees (paid to miners to process the transaction), these fees are typically lower than those of traditional banking services, especially for large sums or international transfers. - Faster Settlement Times
Bitcoin can significantly speed up the process of sending payments across borders. Unlike traditional payment systems that can take days to process, Bitcoin transactions are settled in about 10 minutes on average.
Although scalability and network congestion issues can sometimes delay Bitcoin transactions, advancements like the Lightning Network are being developed to allow for near-instant, low-cost payments by creating an additional layer on top of the Bitcoin network. These improvements could make Bitcoin a highly competitive alternative to current cross-border payment systems. - No Currency Conversion
One of Bitcoin’s most appealing features is that it is not tied to any national currency, which eliminates the need for currency conversion in cross-border payments. A Bitcoin payment made in one country can be received anywhere in the world without being subject to exchange rates. This feature not only saves money on conversion fees but also simplifies the process for both the sender and recipient.
This is especially beneficial in the EU, where transactions between eurozone and non-eurozone countries often require costly conversions. - Banking the Unbanked
Bitcoin’s decentralized nature means that anyone with internet access can participate in the Bitcoin network, regardless of whether they have a bank account. This opens up financial services to individuals and businesses in countries or regions with limited access to banking infrastructure.
For European countries with less developed banking systems, such as those in Eastern Europe, Bitcoin offers a way to participate in the digital economy without relying on traditional banks. This could potentially boost cross-border trade and financial inclusion across the EU.
Challenges to Bitcoin’s Widespread Adoption for Cross-Border Payments

While Bitcoin holds great promise for solving cross-border payment challenges, there are several obstacles that must be addressed before it can become a mainstream solution:
- Volatility
Bitcoin’s price volatility is one of the biggest barriers to its adoption as a payment solution. The value of Bitcoin can fluctuate dramatically in a short period of time, making it difficult for businesses and individuals to rely on it for stable transactions.
Stablecoins—cryptocurrencies that are pegged to stable assets like the euro or dollar—could offer a potential solution to this issue, providing the benefits of cryptocurrency without the price swings. - Regulatory Concerns
The EU has been proactive in regulating cryptocurrencies, and the upcoming Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation will likely impose stricter rules on how Bitcoin is used in the EU. While regulation is necessary to protect consumers and prevent illegal activities, it may also slow down Bitcoin’s adoption as a cross-border payment solution if regulations become overly restrictive.
Additionally, concerns over anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements could create barriers for individuals seeking to use Bitcoin for cross-border payments. - Scalability Issues
Bitcoin’s network is still evolving in terms of handling a large volume of transactions efficiently. While it is secure and decentralized, Bitcoin’s transaction throughput is relatively low compared to traditional payment systems like Visa or Mastercard.
Solutions like the Lightning Network offer hope for scaling Bitcoin’s capacity, but widespread adoption of these technologies is still in its early stages. - Merchant Acceptance
For Bitcoin to become a viable solution for cross-border payments, it must be widely accepted by merchants across the EU. While many businesses are beginning to accept Bitcoin, it is still far from being a ubiquitous payment method. Increasing adoption among retailers and service providers will be key to Bitcoin’s success as a cross-border payment solution.
The Future of Bitcoin and Cross-Border Payments in the EU

Despite the challenges, Bitcoin’s potential to revolutionize cross-border payments in the EU is undeniable. As blockchain technology matures, and as solutions to scalability and volatility are implemented, Bitcoin could become a powerful tool for creating a more efficient, affordable, and inclusive cross-border payment system.
For individuals and businesses looking to avoid high fees, long wait times, and complicated currency conversions, Bitcoin offers a glimpse of a future where cross-border payments are frictionless. However, for this vision to become a reality, both technological advancements and regulatory frameworks must evolve in a way that encourages innovation while ensuring security and stability.
As the EU continues to push for a more integrated digital economy, Bitcoin may well find its place as a key player in the future of European finance.
Conclusion
Bitcoin has the potential to address many of the cross-border payment challenges that persist in the EU, including high fees, slow processing times, and limited access to banking services. Its decentralized, borderless nature makes it an attractive option for a more efficient and transparent payment system.
However, for Bitcoin to become a widespread solution in Europe, issues such as price volatility, scalability, and regulatory concerns must be tackled. If these challenges can be overcome, Bitcoin could help the EU create a more seamless, inclusive, and forward-thinking cross-border payment ecosystem.

